How to Read Pressure on a Barometer
Finding out the conditions forecast these days is as easy as turning on the Idiot box or checking your telephone. That wasn't always the instance, though. In the hundreds of years before telly and even radio, people used more than rudimentary devices to predict what the skies would bring in the coming days.
Ane of those tools was the barometer. Once common in aircraft, ships, and ordinary households beyond the earth, it predicts approaching conditions by measuring changes in air pressure. While technological advancements have replaced the humble barometer in meteorological circles, they're nevertheless fun to have at home and know how to read.
In this article we offer a primer on the history of barometers, how they work, and how to utilise one today to predict the weather. Barometers allow y'all to experience more continued to the natural forces at work exterior your window, and free you from being completely reliant on those oft-wrong apps and local forecasts (studies have shown that local meteorologists inflate the chances for poor atmospheric condition considering it garners better ratings!).
A Brief History of the Barometer

What started every bit an experiment in 1640 to prove the existence of natural vacuums led to the discovery of atmospheric pressure. In 1643, Evangelista Torricelli filled a long tube with mercury, closed the end, and placed information technology in a shallow, open cistern that likewise contained mercury. When the tube was opened, mercury flowed out and filled the cistern, but then stopped about a quarter of the way downwardly the tube and didn't continue to pour out. Something had to be pushing down on the mercury in the cistern to make information technology stop, and that something turned out to be the atmosphere itself, which had previously been believed to be weightless. Then the first barometer was born.
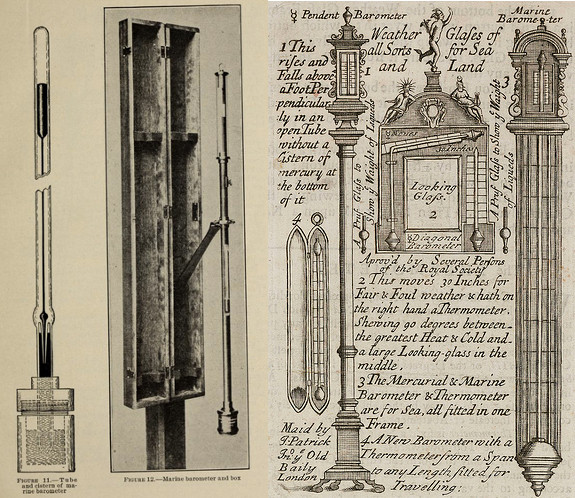
As seen on the correct, looking glasses (mirrors) were often placed almost barometers and thermometers, as they helped people make up one's mind what apparel they were going to put on that day!
In just a couple decades, the instrument became available to well-to-do gentlemen and scientists of both the professional and amateur multifariousness. Woodworkers in the late 17th century took great pride in fashioning elaborate housings for these new atmospheric condition devices, and it became a popular sign of wealth and nobility to brandish a barometer in one's home. The founders of our country were among those addicted of them; both Washington and Jefferson made daily recordings of the air pressure in their journals.

In 1840, the first mechanical, non-liquid barometer was invented. It rapidly took hold, not considering of the concerns about mercury (like there are today), only considering of the simplicity of transporting these devices. They were much smaller and therefore cheaper, as mercury barometers had to exist at least 3 anxiety tall for the air pressure to even out the liquid force per unit area, which is necessary for the musical instrument to work. By 1900, the mercury barometer was largely replaced by these mechanical, or aneroid, versions, and barometers became more than accessible for the common citizen.
Upwardly through the 17th century, making forecasts from the data gleaned from barometers remained a very imprecise scientific discipline; near all they did was predict storms when the mercury rapidly fell, and no one really understood the scientific discipline of weather condition and atmospheric pressure yet. It wasn't until the mid-1800s that English sea captain Admiral Fitzroy did some extensive experiments with his barometers and came upwards with the get-go detailed forecasting tables. He is at present credited with starting the weather forecasting industry and he discovered the predictive significance of rise and falling barometric pressure (which we'll get to shortly). At the same time Fitzroy was at piece of work, meteorologists and weather hobbyists all beyond the world were calculation to the data and the scientific understanding of how weather systems operate and move past trading letters with their fellow observers.

Once the telegraph was invented, and this swapping of data became far easier, conditions forecasting really took off. Conditions observations and data could now be speedily transmitted and therefore graphed and analyzed. Forecasts slowly became more accurate, and noting how the ability to predict storms and frosts saved lives and aided commerce, agriculture, and the military, the government founded the Weather Bureau (at present the National Conditions Service) in 1870. Hundreds of Conditions Bureau meteorological stations effectually the land relied on readings from barometers, thermometers, hygrometers (measuring humidity), equally well every bit observations from the field and at ocean, to offer forecasts to farmers, sailors, and ordinary citizens.

Meteorologists continued to apply traditional barometers well into the mid-1900s.
It wasn't until the mid-20th century that computers began to be used in weather forecasting, and the utilise of traditional monitoring tools like the barometer really declined. While pressure readings are still obviously a major part of forecasts, it's washed digitally rather than by the manual assay of readings.
While "analog" barometers are no longer employed by professional meteorologists, knowing how to use one is a bang-up skill to have. And the first pace towards gaining that know-how is understanding what atmospheric pressure actually is.
What is Atmospheric Pressure level?
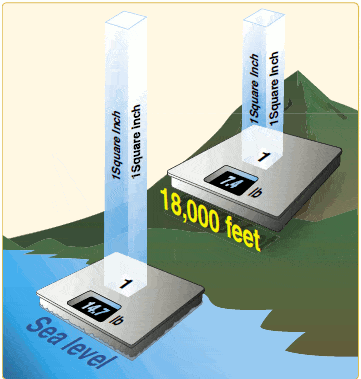
Air pressure decreases as distance increases.
Atmospheric pressure level — or barometric pressure — is simply the weight of the air at ground level. It'south a little easier to understand when you recall most the concept of water pressure level outset. Every bit you get deeper in h2o, the pressure increases. This is because as you descend, the built up weight of the water on top of yous increases. In 1 foot of h2o, you have the weight of that human foot of water pressing downwards on yous. In ii feet of h2o, you have the weight of an extra foot of h2o pressing on y'all. It's quite logical, really.
Now, think of land as being the lesser of the atmospheric ocean. As was proven by Torricelli, air is not weightless. And then barometric pressure is the weight of the air from the top of temper all the manner downwards to y'all. Understandably, pressure level is lower equally y'all go higher in meridian — there's less air on acme of you.
Atmospheric pressure is by and large measured in inches of mercury (in America, that is — it's in millibars in metric nations), which goes back hundreds of years to Torricelli's mercury barometer, which in bones class was still used up until the last decade or so. With the dangerous liquid now being outlawed in most places, and more mod barometers taking agree, the measurement is starting to be replaced by what'southward chosen hectopascals. It is basically a measurement of pounds per square inch, which is more than accurate to what's really happening with the air. Either way, on any consumer barometer you see today, your measurement will be in inches or millibars.
Now that nosotros know what pressure is, let's see how it affects our weather condition. Or more accurately, how the weather affects air pressure.
How Weather Affects Air Pressure
I of things you see most oftentimes in weather forecasts is big "H" and "50" signs moving beyond a map. These are large swaths — usually many hundreds of miles across — of high or depression pressure. There's no number which indicates loftier or low; it's merely a relative term — an area of high pressure is higher than what's around information technology.
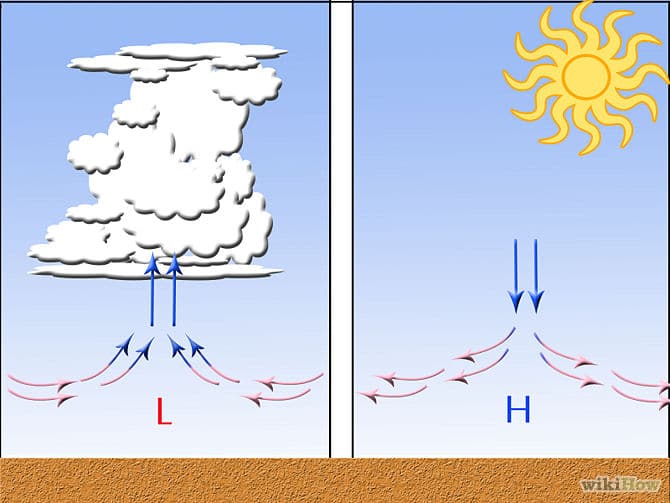
An area of high pressure — i.e. more than down force — pushes air downward. As the air descends, it warms, which inhibits the formation of clouds and tempest systems. So high pressure is almost ever a sign of adept or off-white weather.
Air, however, wants to ascent. So once it hits an area of depression force per unit area — where downward strength isn't as bang-up — it volition accept that chance. As the air rises, information technology cools, which condenses and forms precipitation. Hence, low force per unit area is associated with poor weather ("poor" is of course a relative term — some folks actually like storms and rain!).
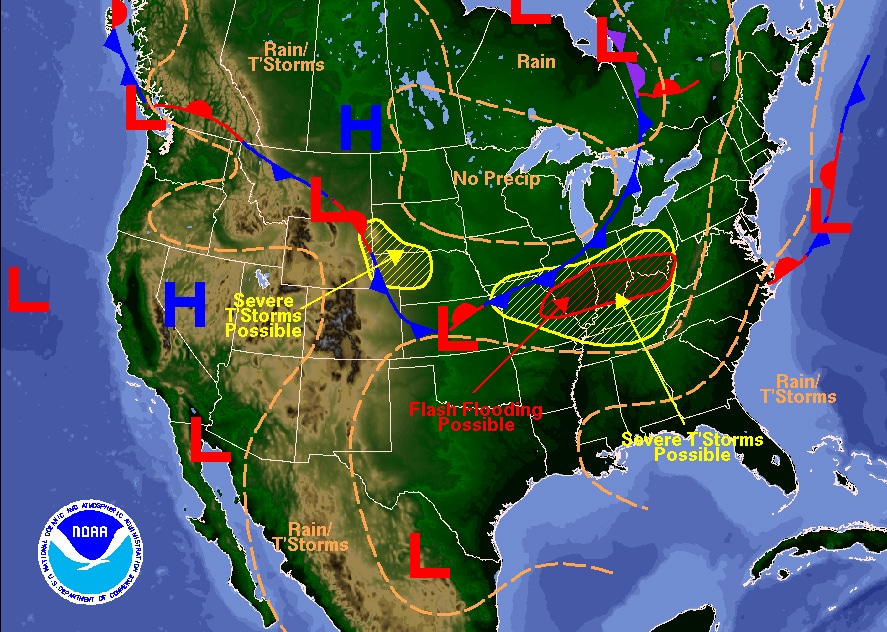
So you can imagine a patchwork of high and low force per unit area swaths beyond a map. These are created by wind, the rotation of the planet, the sun — all kinds of factors that are completely outside of human being control or prediction. But what we exercise know is the type of weather condition that these differences in air pressure level portend.
A barometer that has a high reading — meaning high force per unit area — and is stable, indicates good weather. You're in the midst of a high pressure organisation. A barometer that is falling indicates that a low pressure level system is moving in, and you can expect poorer weather. How bad that conditions becomes is the consequence of how great the difference is between the loftier pressure and low force per unit area organization. The bigger the divergence, the more than volatility there is in the temper, and the stronger the tempest. The smaller the difference, the less likely you are to see pelting or storms.
Alright — you lot know nigh air pressure level, and how information technology's affected past the weather. Now we can learn about the types of barometers, and how to actually use them to predict the weather.
Types of Barometers
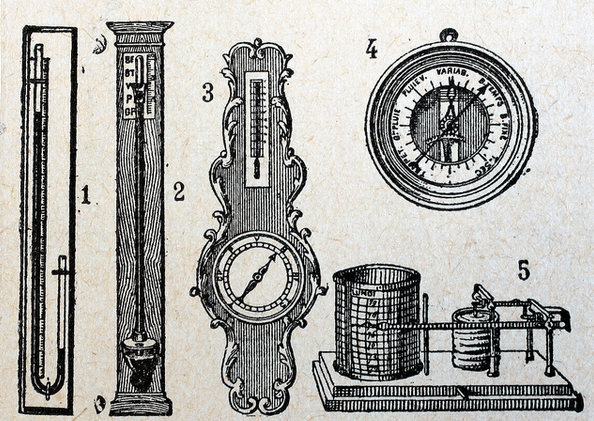
Through the years, diverse types of barometers accept been used to help weather forecasters and seamen akin. Permit's briefly take a look at them and how they work:
Mercury: As we know, this was the get-go barometer invented. It utilizes an open mercury cistern along with a closed tube at least thirty inches in acme. The air presses on the open mercury, which raises or lowers the level of the mercury in the tube. Considering of its use of a dangerous substance, you tin't discover new models on the market place today. There are modern versions that have basically the same machinery, but use neither mercury nor an open up pool, but rather a stock-still corporeality of gas enclosed in the tube. Ultimately, these aren't equally accurate equally modern versions.
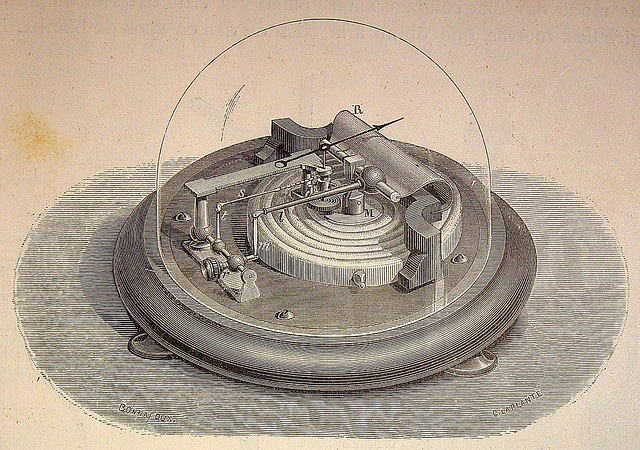
Aneroid: Invented in 1844, the aneroid barometer is a non-liquid device. Information technology utilizes a minor metallic box — called an aneroid prison cell — made from an alloy of glucinium and copper. Changes in air pressure level crusade the box to aggrandize or contract, which drives mechanical levers that are then displayed on the face of the barometer. These are often the beautiful devices that yous imagine seeing in old ships and weather condition stations, and are yet used today in many cases.

Electronic: As with every tool in our modern historic period, barometers used in modernistic navigation and meteorology are generally electronic. How they work is a flake difficult to empathize, then I had to ask meteorologist and professor Jon Van de Grift to give it to me in the nigh layman way possible: "Electronic barometric sensors provide the user with an estimate of elevation to a higher place sea level. These incorporate a strain gauge, which is a thin wire that changes its electrical resistance as a outcome of atmospheric pressure level acting on a diaphragm wrapped effectually it. The resulting alter in voltage can be amplified and read by a converter, and eventually displayed to the user."
Which Type Should You Buy?
To my surprise, finding a barometer was incredibly challenging. There simply aren't many options.
The commencement option — and the best for the true meteorologist — is to find a digital weather station, which will likely include a barometer, every bit well as other readings like temperature and humidity. You tin sometimes get these at big box stores, sporting goods stores, and even nurseries/floral shops, only you are probable to exist limited to merely 1 or 2 models to choose from. Your better bet is buying one online, similar this one. It has a sensor that you hang outside which so sends measurements to a digital reader.
The other option, besides buying an antique, is to get a handsome looking aneroid barometer from an online retailer. I looked all over town for one, and couldn't get my hands on anything. And that's in Denver — it's not like it's a small town. I ended upward getting this model from Fischer. Aneroid barometers work really well, and look darn good on a wall as a manly decoration piece. It doesn't matter if they're within or exterior, but know that some things volition affect readings, such as proximity to heating or cooling vents, also equally utilize of air conditioners or humidifiers.
How to Use a Barometer to Forecast the Weather
At present that you know the scientific discipline, being able to forecast the weather is really rather unproblematic. And while there are some differences in using an aneroid or digital barometer, the principles in measuring and analyzing pressure are the same.

The back of an aneroid barometer. The holes at the top of plastic backing allow for air to flow through. The small spiral on the bottom right border is what's used to calibrate the device; I had to employ a small eyeglass screwdriver to practice then.
Setting up your barometer is easy. For an aneroid version, you need to manually calibrate information technology. All this ways is using a small screwdriver to set the hand (like on a clock) to lucifer the current barometric pressure in your location (I use weather.gov). In one case you've washed that, it'south all fix.
Digital barometers — normally included equally office of a more comprehensive amateur weather station — do that office for y'all.
As we already learned, barometer measurements will either exist in inches or millibars. Readings volition more often than not be between 28 and 31 inches, ordinarily measured to the hundredth decimal. Knowing just the number itself, however, isn't all that helpful. What matters is in which direction the needle is moving. It's the change in barometric pressure that helps forecast the weather. This means that static numbers with no indication of rising or falling aren't generally very useful.
So, to become accurate predictions, you demand to have a await at the barometer every few hours and come across how the number is changing. Keep in mind that changes will seem miniscule; in the few weeks I've had my barometer it'southward been between xxx.00 and 30.30 the entire time, normally only moving .05-.ane in either direction on whatsoever given twenty-four hours.
On an aneroid barometer, you'll have 2 easily. One will show the barometric force per unit area reading, and the other is a manual punch that y'all align to the pressure reading whenever you take a measurement. The purpose of the manual manus is so that yous can chop-chop and easily meet which management the needle has moved, and how far, betwixt readings:

Conform the dial on an aneroid barometer whenever you lot take a reading to align the manual hand with the measurement mitt.

And then, next time you lot take a reading, yous can speedily come across which direction the measurement needle has moved. The electric current reading here is about 30.18 inches.

Aneroid barometers also usually have layman's terms like "Stormy" and "Dry out" on them. The idea is that barometer readings at sure levels will portend those weather conditions. Unfortunately, those terms really only work at bounding main level. Hither in Denver — a mile above ocean level — they're about worthless. No matter to me — they add together to the decorative appeal of the barometer.
On a digital barometer, you'll most probable accept indications of "rising" or "falling," and perchance even a graph — called a barograph — showing previous readings and trends. This will be more helpful and accurate for the true amateur meteorologist. Rather than having to chart or retrieve previous readings, the device does it for you.
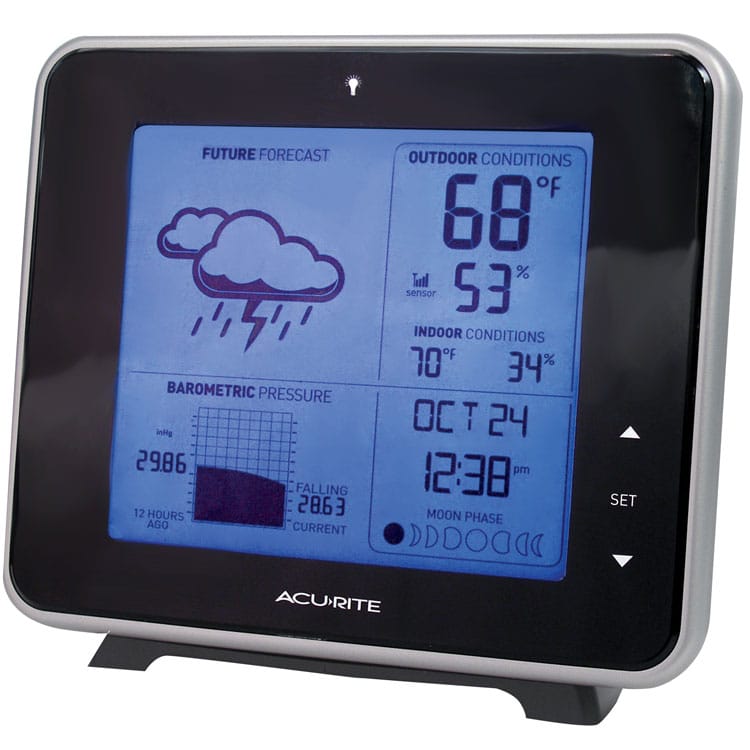

You can see the barometer reading in the lower left corner of this digital conditions station. It includes a graph — chosen a barograph — which shows trends and movements in pressure.
Beneath is a basic chart which shows barometer readings and their correlated weather patterns to assistance you get started. Keep in mind that every location is different, and that a number of things impact a barometric reading, including temperature, meridian, humidity, etc. In an atmospherically volatile location similar Denver — with the mountains apace affecting weather systems — some storms form too quickly to exist picked up on. That's just the nature of weather condition! Likewise keep in listen that barometers will only assist you forecast for the side by side 24-48 hours or so. Since pressure systems last days and sometimes weeks, it tin be a while before you notice any substantial departure in your readings.
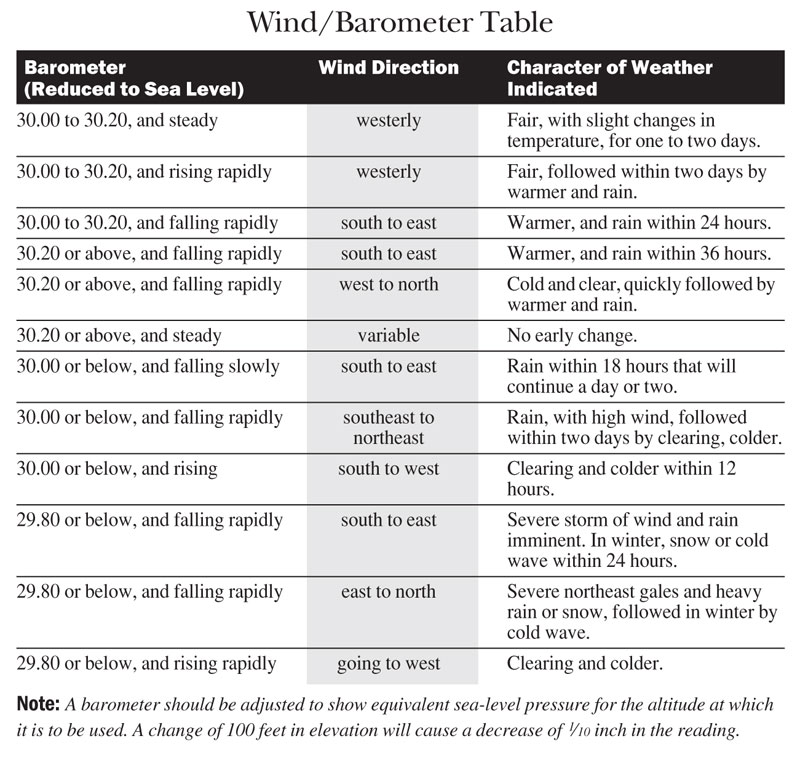
These are readings for sea level. Y'all tin can utilize this estimator to adjust for your elevation. In my experience, rather than the numbers themselves, the rise and falling trends are more important. You'll come to observe the how and low points of the atmospheric pressure level in your expanse, and soon be able to non rely on the nautical chart.
After a few weeks of taking readings, you lot'll come to know your local atmospheric condition pretty well, and you'll be able to determine what's high, what'south low, what'due south surprising, etc. Get out there and get forecasting!
Previous Adjacent
Source: https://www.artofmanliness.com/lifestyle/gear/fair-or-foul-how-to-use-a-barometer/
0 Response to "How to Read Pressure on a Barometer"
Postar um comentário